3D Shape Reconstruction under Participating Media
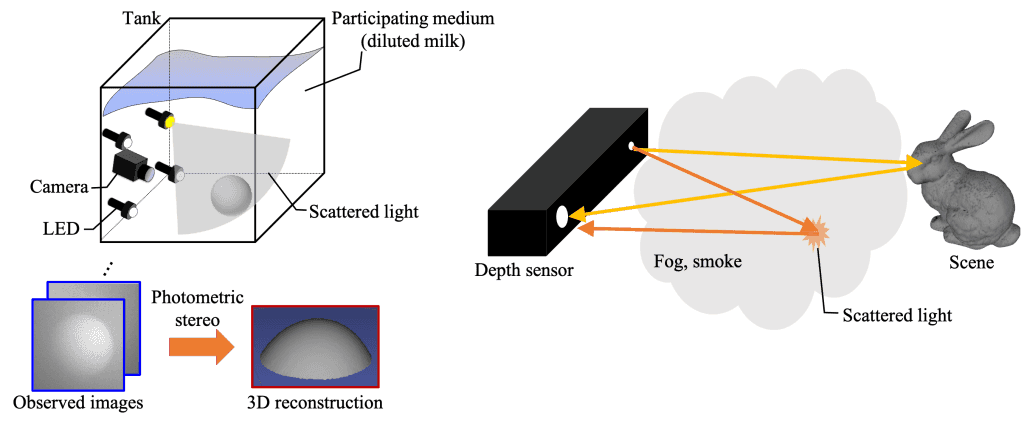
3D reconstruction is a technique to reconstruct an object’s 3D shape from 2D images captured with cameras. This technique can be utilized for a variety of applications such as self-driving vehicles and AR/VR technology. We develop 3D reconstruction techniques in participating media. For example, the contrast of an image captured under murky water, fog, or smoke is corrupted by scattered light due to suspended particles. 3D reconstruction techniques in such environments enable various applications in the real world.
3D reconstruction in participating media
Overview
3D reconstruction is a technique to reconstruct an object’s 3D shape from 2D images captured with cameras. This technique can be utilized for a variety of applications such as self-driving vehicles and AR/VR technology.
We develop 3D reconstruction techniques in participating media. For example, the contrast of an image captured under murky water, fog, or smoke is corrupted by scattered light due to suspended particles. 3D reconstruction techniques in such environments enable various applications in the real world.
Photometric stereo in participating media
Photometric stereo reconstructs surface normals using several images captured under different lighting conditions. We proposed the physical model of light scattering for photometric stereo in highly turbid water. This technique can be utilized for visual inspection in participating media or autonomous underwater vehicles.
Depth sensing in participating media
A depth sensor measures scene depth by illuminating the scene and observing the reflected light. In participating media, however, the accuracy of the depth measurement is deteriorated because the sensor also observed scattered light. We used Microsoft Kinect v2 for detecting objects and estimating the depth in foggy scenes. The proposed method enables simultaneous automatic obstacle detection and depth reconstruction in challenging environments such as disaster sites.